Macros 101: What They Are, What They’re For
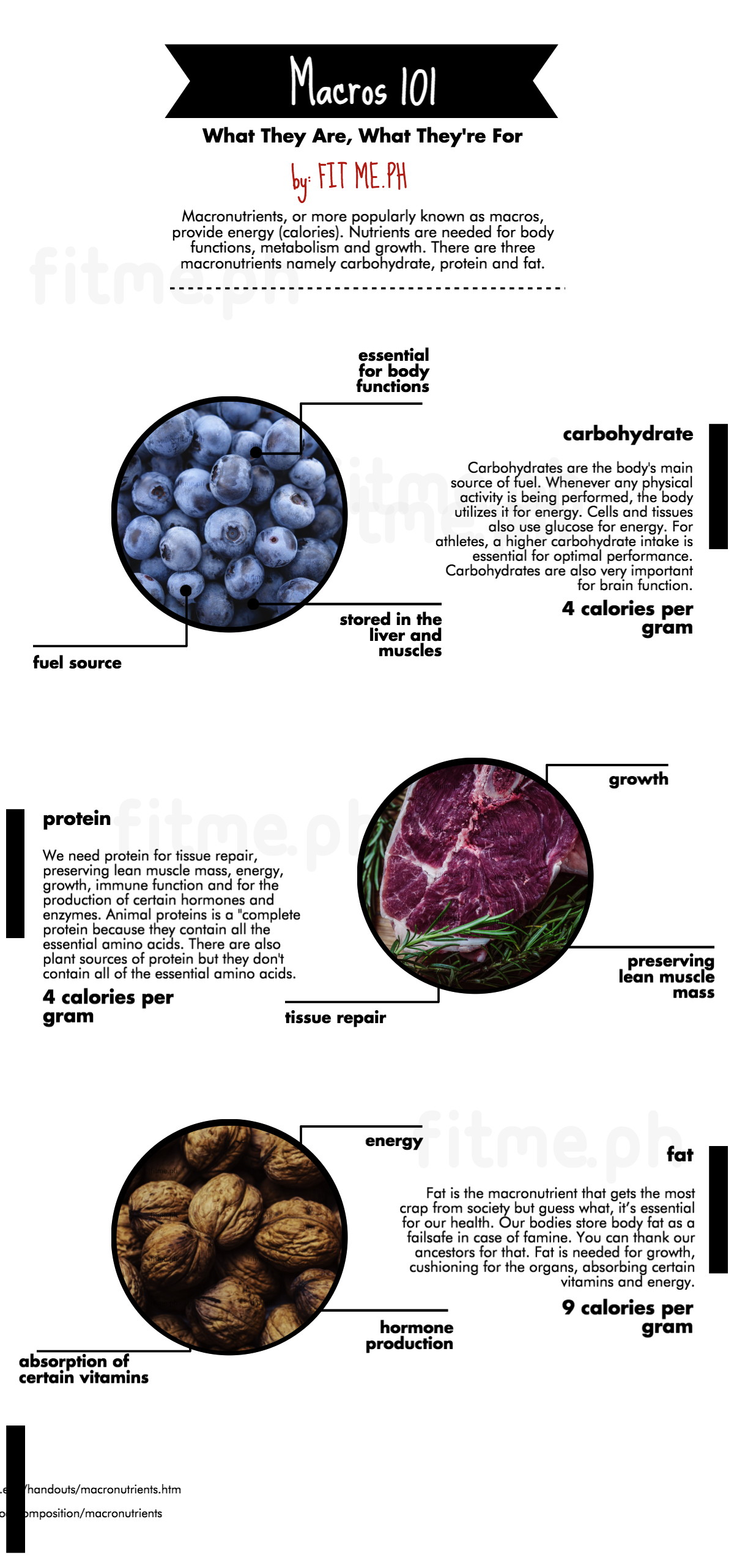
Macronutrients, or more popularly known as macros, provide energy (calories). Nutrients are needed for body functions, metabolism and growth. There are three macronutrients.
- Carbohydrates
- Protein
- Fat
Carbohydrates
Your body’s go-to fuel source
Food sources rich in carbohydrates:
- Rice (white, brown, red, black…)
- Bread
- Pasta
- Potatoes
- Oatmeal
Carbohydrates are easily absorbed and are the body’s main source of fuel. Whenever any physical activity is being performed, the body utilizes it for energy. It is stored in the liver and muscles. All cells and tissues use glucose for energy. Carbohydrates are also important for brain, kidney, central nervous system and brain function.
What about fiber?
Fiber passes through the intestinal tract to help with waste removal. Low-fiber diets have been shown to increase risk for certain types of cancers, and may cause problems such as hemorrhoids and constipation. On the other hand, diets high in fiber have been shown to lower cholesterol and decrease risks for obesity and heart disease.
Protein
Your body’s go-to source for building and repair
Food sources rich in protein include:
- Chicken
- Beef
- Fish
- Eggs
- Milk
- Soy
- Nuts
We need protein for tissue repair, preserving lean muscle mass, energy, growth, immune function and for the production of certain hormones and enzymes. Animal proteins is a “complete protein because they contain all the essential amino acids. There are also plant sources of protein but they don’t contain all of the essential amino acids.
Fat
Your body’s energy stores
Food sources rich in fat include:
- meat
- poultry
- nuts
- oils
- milk products
Fat is the macronutrient that gets the most crap from society but guess what, it’s essential for our health. Our bodies store body fat as a failsafe in case of famine. You can thank our ancestors for that. Fat is needed for growth, cushioning for the organs, absorption of certain vitamins, hormone production and energy.
What is a Calorie?
A calorie is a unit of energy that can be consumed or be used to function. When you consume calories, you’re giving your body energy to be utilized. For example, consuming a banana will supply your body with 90 calories. Those 90 calories can be stored by the body or used for energy depending on your activity levels throughout the day.
Convert Macros to Calories
| number of calories | |
| Protein | 4 |
| Carbohydrates | 4 |
| Fat | 9 |
Sources:
http://www.mckinley.illinois.edu/handouts/macronutrients.htm
https://fnic.nal.usda.gov/food-composition/macronutrients
Please share if you found this article helpful!
 FITME.PH Fitness + Lifestyle + IIFYM
FITME.PH Fitness + Lifestyle + IIFYM